AArc141/14/EVAL Roussillon Park, Broyle Road, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 BBL
Sporadic finds represent the early prehistoric period in the vicinity of the Project Site, with
the discovery of Palaeolithic axe in a garden on Brandy Hole Lane (c. 600m to the NW)
and a Neolithic stone axe, in the vicinity of Spitalfield Lane, over 1km to the SE (Lee 2008:
9).
Bronze Age activity has been recorded c. 500m to the east of the site, in the vicinity of
Garyiingwell Hospital, where evidence for settlement was identified along with remains of
six cremation burials (Lee 2008: 9).
The Iron Age is strongly represented in the vicinity of the Project Site, in the form of
earthworks (entrenchments) which may follow the route of The Broadway, which borders
the development area, 500m to the north. Excavations at Garyiingwell Hospital may have
identified a continuation of this defensive system (Lee 2008: 9). In addition, Iron Age
settlement has been identified c. 1km to the north, bordering Broyle Road where hut
circles and ceramics have been identified (English Heritage Ref SJ80 NE8).
Romano-British (AD 44 — AD 410)
Archaeological investigations c. 500m to the SE of the Project Site have revealed
evidence of early Roman settlement, in the form of a ditch (EH Ref 1333100), earthwork
features, a hearth and a probable Roman Kiln (EH Ref 1336313). Evidence of settlement
in the Roman period has also been identified in the vicinity of Garyiingwell Hospital and
adjacent to Broyle Road, 900m to the north of the Project Site. In addition, Archaeology
South East identified a cremation cemetery adjacent to Broyle Road, c. 600m to the south
(Lee 2008: 10).
Furthermore, a Roman Road has been identified, running from the north gate of Roman
Chichester (Noviomagvs Regnensivm), to Silchester (Calleva Atrebatum), potentially
following the SW—NE route of modern day Norwich Road, 600m SW of the Project Site
(Wacher 1976: 254).
Saxon - Medieval (AD 410 — AD 1540)
There is very little recorded evidence for early medieval activity in the vicinity of the
Project Site. Lee highlights the site of Chichester Priory, 1km to the SSE and the
discovery of a Saxon spearhead, 600m to the north (Lee 2008: 10).
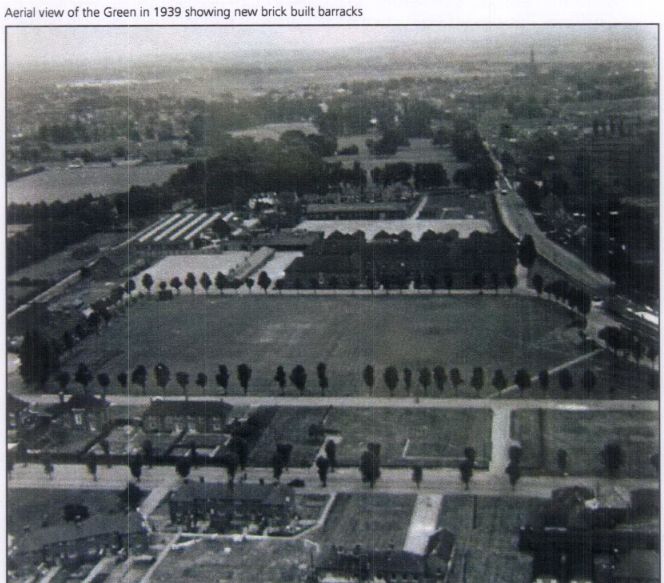
Changes to the landscape in the mid to late medieval period are more widely represented.
The Project Site represents part of deer park, granted to the Bishop of Chichester in the 16”‘ century.
The land is documented to have remained in the ownership of the church
until the barracks were established on the site in the 18”‘ century (Lee 2008: 10).
Post-medieval (AD 1540 — AD 1900)
In the post medieval period the site continued to be used by the military. The most
significant evidence for this period with regard to the development of the site is provided
by cartographic and documentary evidence of the location of the town gallows. 19”‘
century maps locate the gallows to the NE of the site. A commemorative stone (now
relocated) was placed on the site in 1789 AD in order to recount the story of the
Hawkhurst Gang, who were involved in smuggling in the area. it is claimed that one of the
gang was buried in a field adjacent to the gallows. The exact location of the burial is
currently unknown (Lee 2008: 11).
The location of the main road heading NE to east Lavant crossed the Project Site prior to
the enclosure ofthe area by the military (pers com J Kenny).
Approach To Archaeological Investigation
The investigation took the form of an archaeological trench evaluation, undertaken to
ascertain information on the presence/absence, extent, state of preservation, character,
quality, integrity and date of any archaeological deposits on the Project Site. The
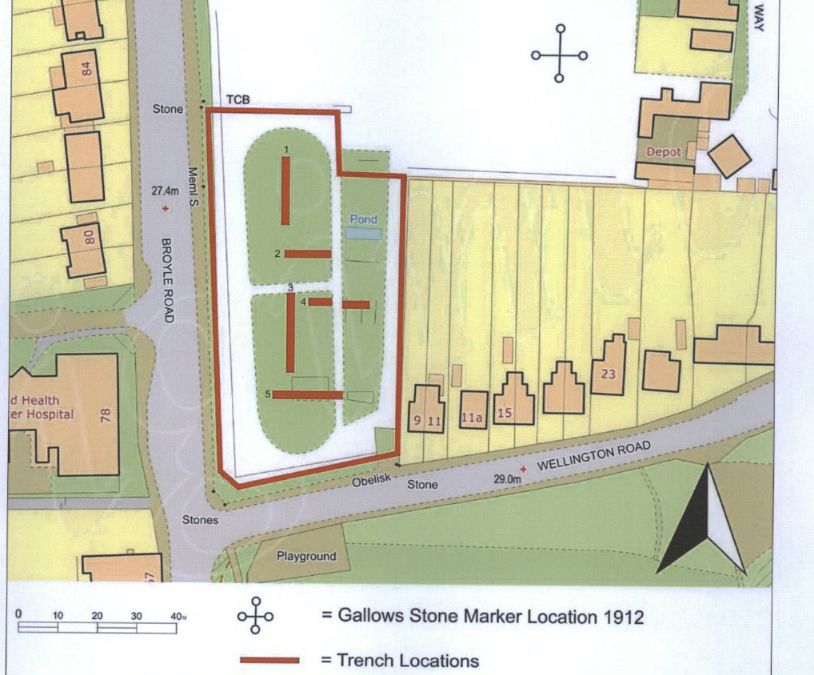
Programme of Investigation comprised the excavation of 5 trenches measuring from ‘l2m
— 20m in length, to the depth of the archaeological horizon or the natural sub strata,
whichever was encountered first. Trench locations and lengths have been altered from the
plan approved in our initial Written Scheme of Investigation. This has been carried out to
accommodate existing drainage and track ways currently in use on the Project Site. All
alterations were approved by Mr James Kenny (Archaeologist, Chichester District
Council), during his site visit. The specific dimensions and details of each trench are
detailed in appendix 1.
All fieldwork was carried out in accordance with the IFA Standard and Guidance for an
archaeological excavation (revised 2008) and Management of Research Projects in the
Historic Environment: PPN 3: Archaeological Excavation (English Heritage 2008).
Broadly the archaeological investigation sought to:
- Assess the potential for archaeological activity associated with the Project Site;
- Establish the date, nature and extent of activity or occupation within the
development area;
Absolute Archaeology 3
AArc141I14IEVAL Roussillon Park, Broyle Road, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 ESBL
0 Record and identify archaeological features and deposits to a level appropriate to
their extent and significance;
- Establish the potential for human burial in the vicinity of the Project Site;
o Undertake sufficient post-excavation assessment to interpret archaeological
features and phasing identified during the investigation and to place these within
their local and regional context;
- Create a site archive for deposition in a suitable repository;
- Inform the implementation of a suitable strategy in order to mitigate the impact of
the groundwork on the archaeological resource, in the event of positive results.
Results
Trench One
Excavation in the area of trench one revealed a topsoil I turf line layer, sealing a deposit of
made ground, which was seen to overlay truncated natural gravels.
Trench Two
Excavation in the area of trench two revealed a topsoil I turf line layer, sealing a deposit of
made ground, which was seen to overlay truncated natural gravels.
Trench Three
Excavation in the area of trench three revealed a topsoil I turf line sealing two truncated
rectangular concrete features, with cut off central iron uprights [301] 8. [302]. The features
appear to be supports for a lightweight structure, perhaps fencing. The concrete features
were set into cuts within the truncated natural gravel.
Trench Four
Excavation in the area of trench four revealed a topsoil I turf line sealing a series of
truncated concrete features, similar to those identified in trench three. Two linear features
[402] & [403] identified bisecting the trench to the east appear to be represented on a
1970’s map (Fig 3). The resource shows a formal oval track with pond and linear features
to the east. Two concrete and iron structures were also identified to the west of the trench.
Trench Five
Excavation in the area of trench five revealed a topsoil I turf line sealing a subsoil layer,
which was seen to overlay the natural gravel.
© Absolute Archaeology 4
Finds
Apart from occasional sherds of residual Post Medieval ceramics recovered from the
topsoil I turf line and made ground material, no artefacts were identified during the
excavation and no finds were recovered from the spoil, which was monitored throughout.
Discussion
No archaeological features were identified during the excavation and results suggest that
the Project Site has been reduced in the past, in line with landscaping in this area in the
19'/’0’s. The evidence of truncated concrete features confirms activity on the site in the
Post Medieval period, which most likely corresponds to the reduction of the natural in the
area of trenches one to four. The features appear to represent supports for lightweight
structures associated with the linears identified on modern cartographic resources.
Evidence of subsoil in the vicinity of trench five suggests that the southern portion of the
Project Site may have experienced a lower level of disturbance. However the shallow
depth of the subsoil suggests that this material has been truncated and that the topsoil
across the site is an imported material.
There was no evidence of the historic main road heading NE to east Lavant, which would
have been located on the region of trench five. Furthermore, no evidence of a burial was
encountered during the trench evaluation. However, it is possible that shallow truncated
features may be preserved across the remainder of the Project Site.
Conclusion
The results of the evaluation confirmed that the archaeological potential of the Project Site
has been significantly reduced by Post Medieval activity. The results of the investigation
were negative and no further investigation is recommended in conjunction with this phase
of the project.
Absolute Archaeoiogy 5
AArc141/14tEVAL Roussillon Park, Broyle Road, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 BBL
8. References
English Heritage. 2006. Management of Research Projects in the Historic Environment
(MQRPHE) — The MORPHE Project Managers Guide. Swindon: English Heritage.
English Heritage. 2011. Environmental Archaeology: A Guide to the Theory and Practice
of Methods, from Sampling and Recovery to Post-excavation (second edition). Swindon;
English Heritage.
institute for Archaeologists. 2008. Standard and guidance for archaeological field
evaluation. Reading: IFA.
Institute for Archaeologists. 2008. Standard and guidance for the collection,
documentation, conservation and research of archaeological materials. Reading: lFA.
Lee, F. 2008. Roussillon Barracks, Chichester Archaeological Desk Based Assessment.
Desk—Based Assessment, Faber Maunsell.
McKinley, J. l. and Roberts, C. 1993. Excavation and Post-Excavation Treatment of
Cremated and inhumed Human Remains (IFA Technical Paper No 13). Reading: lFA.
Margary, l.D. 1973. Roman Roads in Britain. London: John Baker.
Wacher, J. 1976. The Towns of Roman Britain. London: Batsford.
© Absolute Archaeology 6