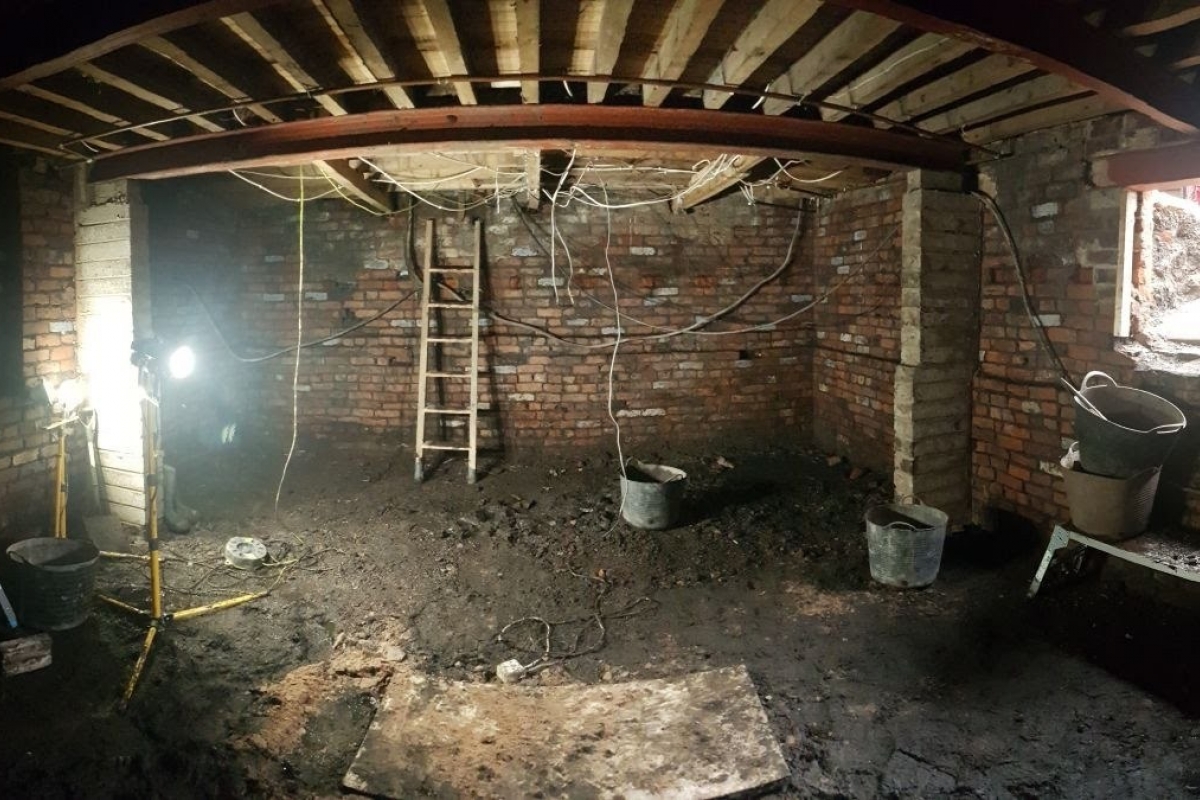
Historically, to build a house with a simple cellar you would dig out the ground to a depth of around 6ft, the cellar walls would have been constructed with a lining of stone or brick and with a drain for water within the cellar. The floors would have been built up on crushed stone or sand to provide a level surface and paved, usually with flags. Brick paving became more common in later periods.
In small buildings the cellars were simply covered by the timber ground floor and ceilings of lath and plaster, but in larger houses arches and barrel vaults were often used to enable the floor above to be paved. If constructed for storage purposes, domestic cellars often have stone benches for salting meat and coal chutes, which are common across the country.
The building of a cellar may have been as follows. Initially, the void would have been dug out and all the spoil removed by spade, windlass and bucket. Then the initial side walls would have been constructed, probably of local stone. The arches to span the cellar would then have been “sprung” across the width of the cellar using scaffolding or centring of timber underneath to support them. Doorways in 0 he walls provided access to neighbouring cellars during contrstruction.
Striking or removing the centring was a dangerous task and It would have taken months to build each cellar, in part because lime mortar would have been used. Lime mortar sets properly only over time, and that time depends on the precise mix used and the local climatic conditions.
It was at that moment that failures in arch building often occurred, either because the lime mortar was insufficiently set or there were constructions faults.
The roof itself was added following construction of the arches by placing planks longitudinally from arch to arch.
extracts from
http://www.rth.org.uk/building-regency-houses/structure/foundations
https://www.buildingconservation.com/articles/damp/damp_cellars.htm